1.2.1 木材声学性质测定
木材振动性能测试:基于梁的振动理论,采用双端自由的边界条件,应用日本小野测器(ONO SOKKI)生产的双通道快速傅里叶变换分析仪FFT(CF-5220Z),在试件的基频振动节点处(距试件端头长度为总长度的0.224倍),用泡沫三角架将试件水平撑起,利用刀片给试材一定的激励,利用微音器收集其声学信号,得到试件的时域以及频域信息,记录试件振动信号前5阶峰值对应频率。试验原理示意图如图1所示。再根据式(1)~(5)计算出试件的动态弹性模量(E)、声辐射品质常数(R)等反映木材声学振动性能的参数[17]。
图1 木材共振频率测定试验原理
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the experimental principle of wood resonance frequency determination
通过弯曲共振法测得的动态弹性模量(E)计算公式为:
E=(48π2ρL4f2)/(m4T2) (1)
式中:ρ为试件密度; L为试件长度; f为试件弯曲共振频率; m为振动阶数所决定的系数; T为试件厚度。
木材长度方向的声传播速度(v)计算公式为:
v=(E/ρ)1/2 (2)
声辐射品质常数(R)表示木材及其制品向周围空气辐射声功率的大小,可评价材料的声辐射能力,其计算公式为:
R=v/ρ=(E/(ρ3))1/2 (3)
对数衰减率(δ)表示木材因摩擦损耗所引起的能量损耗,自由振动时:
δ=ln(A1)/(A2) (4)
式中,A1和A2为两个连续振动周期的振幅。
声阻抗(ω)是表征介质性质的重要物理量,其计算公式为:
ω=ρv (5)
1.2.2 小波包分析
小波包分析是小波分析的延伸,其基本思想是使信号的信息能量集中,为信号提供一种更加精细的分析方法[18]。小波包变换中的Daubechies系列小波是目前工程应用最广泛的、最成熟的正交连续且紧支撑的小波函数族。Daubechies小波是由小波分析学者多贝西提出的二进小波函数,用dbN表示(N为小波的阶数)。由于其尺度函数为低通函数且长度有限,因此Daubechies小波具有低通滤波器的特性,又因木材的能量主要分布在低频段,所以在本研究中选择Daubechies小波基符合木材振动信号的特点。基于Daubechies小波基对木材振动信号进行小波包分析,主要是利用小波包能量的分解与重构,将隐含的木材振动信号的特征分量提取出来,并将其映射到不同的频带上,通过对比分析不同频带能量分布的情况,可以体现不同木材振动信号的差异性,从而获取不同木材振动信号的特征与其声学性能之间的定量关系。
对信号S(t)进行小波包分解后,在第i分解层可得到2i个子频带,S(t)的表达式为:
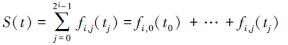 (6)
(6)
式中:S(t)为总信号; fi,j(tj)是将木材振动信号小波包分解到相应节点(i,j)上的重构信号,其中,j=0,1,2,…,2i-1(i=1,2,3)。
由式(6)和巴什瓦(Parseval)定理可以得出第i层信号中的能量,其表达式为:
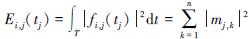 (7)
(7)
式中:i、j分别表示小波包分解的层数和采样点数; Ei,j(tj)表示信号在第i层第j个节点处的小波包子频带能量,其中,mj,k(j=0,1,2,…,2i-1; k=1,2,…,l)表示木材振动信号分解后得到的重构信号fi, j(tj)离散点的幅值,在分解的第i层,有2i个子频带。
峭度因子(K)和峰值因子(C)是对振动信号进行时域处理最常用的无量纲参数指标,通过MATLAB软件输入相应程序可直接计算出来。峭度因子通常用于检测振动信号中的冲击成分,其定义为:
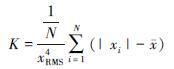 (8)
(8)
式中:xi为振动信号幅值;(-overx)为振动信号平均值; xRMS为振动信号的有效值。通常在振动信号分析中引入能量的观点,实际上,振动是能量的一种表现形式,有效值则反映了试材振动能量的状况,其计算公式为:
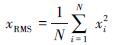 (9)
(9)
峰值因子可表示振动信号的峰值在波形中的极端程度,其定义为:
C=(xp)/(xRMS) (10)
式中,xp为振动信号的峰值。
木材振动信号的处理:笔者选用应用较多的dbN小波函数系,它的优点是随着N值的增加,支撑长度变长,频率局部性变好,同时其滤波器长度增加,但随着N值的变大,dbN小波系的计算量呈指数增加,因此,在本试验中选用db4[19]小波对木材振动信号作3层小波包分解。在MATLAB的Wavelet Toolbox中用db4小波对木材时域振动信号进行3层小波包变换,并对变换后的信号进行重构,获得信号在不同频段的能量分布。测试选取的频宽为8 kHz,信号的采样频率为频宽的2.56倍,即20.48 kHz,把振动信号经过3层小波包分解,将振动信号划分为8个等带宽的频段,所以式(7)中的i=3,振动信号的采样点数j=2 048,并对第3层的系数进行重构,以重构信号小波包系数能量值作为研究对象,提取信号在不同频段的能量特征分量,计算各子频带能量的占比,滤掉其他分量的干扰信号,得到信号特征与木材声学参数之间的相关性,进而分析其与木材声学性能之间的关系。